To increase job interview success, career professionals need be aware of their own interview identity – how the applicant is perceived by the interview panel during the recruitment process.
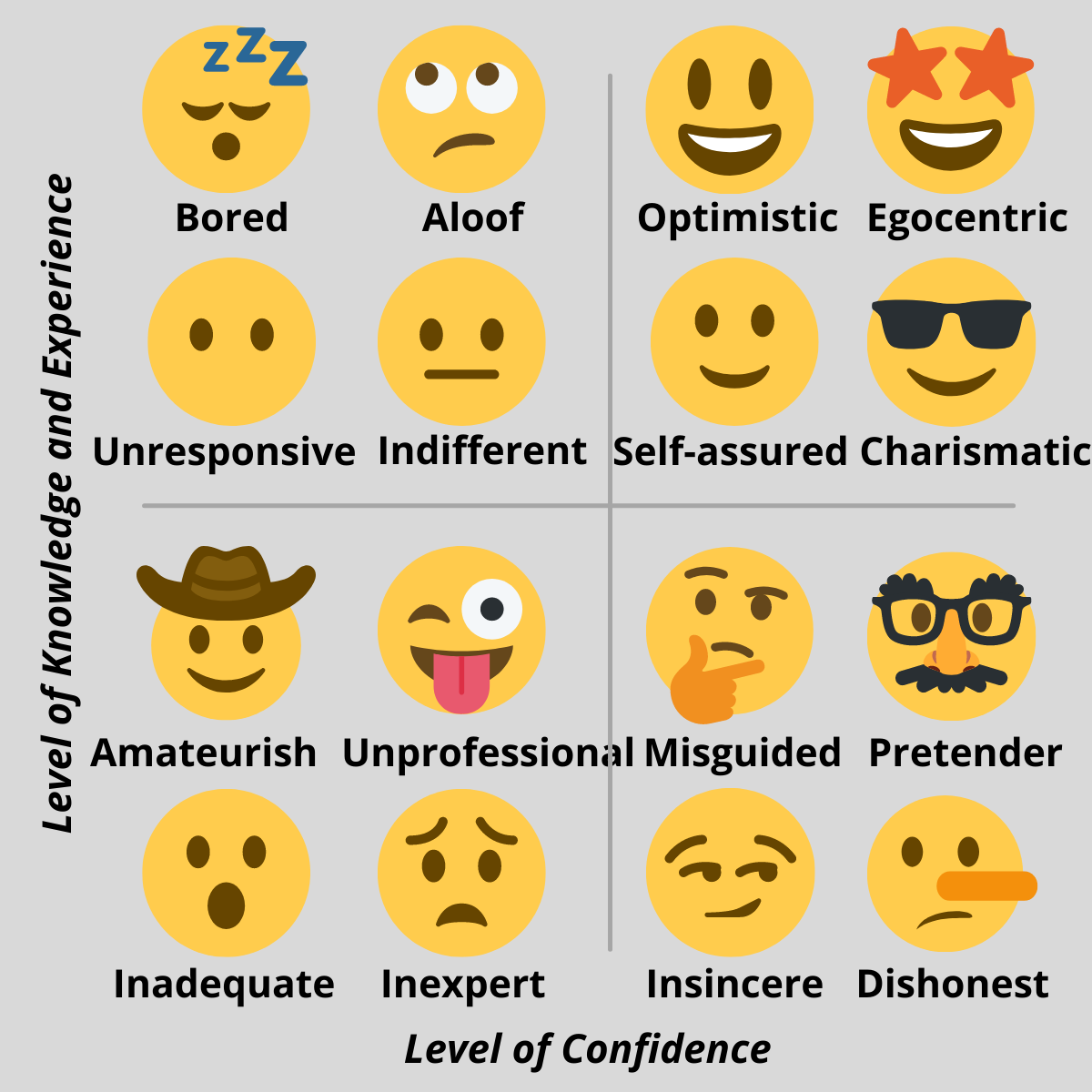
The 16 interview identities sit within 4 overarching identity categories, based on the candidates perceived level of knowledge and experiences vs the applicants level of confidence.
The two axes, knowledge/experience and confidence, have a low to high scale. The 4 interview identity categories create a generic opinion.
- Low level of knowledge/experience and a low level of confidence
- Low level of knowledge/experience and a high level of confidence
- High level of knowledge/experience and a low level of confidence
- High level of knowledge/experience and a high level of confidence
It is important to remember that the interview identities have no relation to a career professionals ability to perform tasks in the real world or work, instead they are the employers perception of the applicants predicted job performance.
“A skilled worker who fails to communicate their competencies confidently can be seen as less skilled then they actually are”.
Chris Delaney author of ‘what is your interview identity’
The four characteristics of an interviewee.
The interview prediction grid model states that there are 16 interview identities that fit into four categories:
- Incompetent (low/low)
- Deceitful (low/high)
- Uninterested (high/low)
- Employable (high/high)
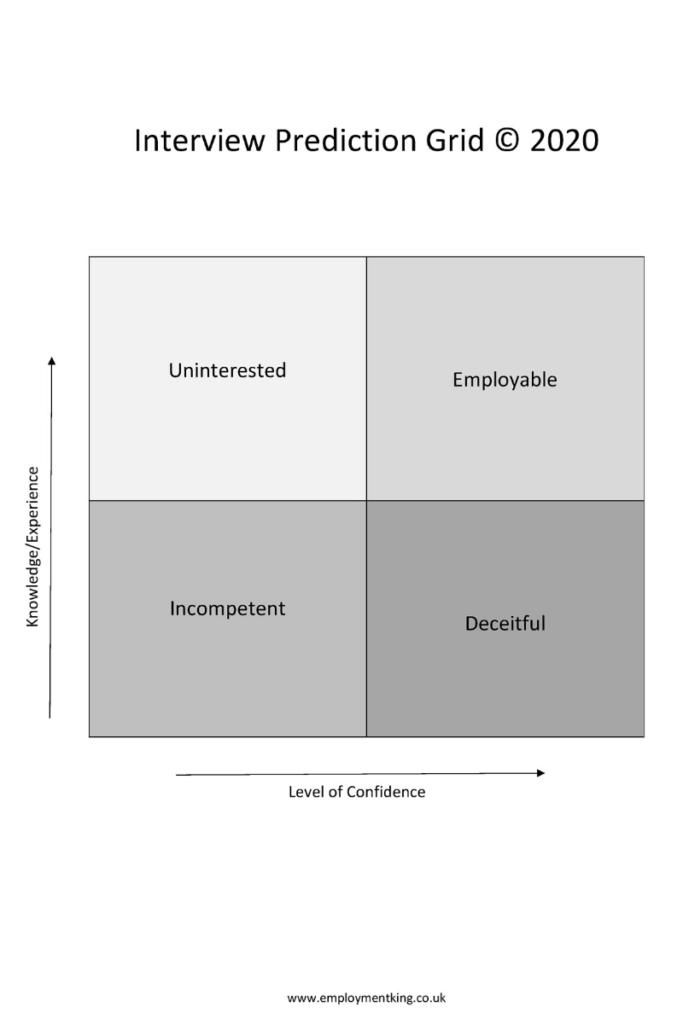
Incompetent
Incompetent job applicants have a lack of job experience and confidence, resulting in a nervous display during the recruitment process and a misunderstanding of the job interview questions.
Deceitful
The deceitful characteristic comes from a high level of confidence with a low level of industry knowledge and experience. They talk the talk, but cant walk the walk, resulting in an increase in destruct.
Uninterested
Career professionals with a high level of knowledge and experience, but who lack the confidence to express their competencies during the interview, can be seen as uninterested in job position – why else would a highly skilled applicant give short snappy answers?
Employable
Being skilled at communicating competencies confidently creates a persona of being employable, or highly employable. Descriptive and detailed answers, delivered well using a number of non-verbal communication skills, creates likability and desire from the interview start.
Take the interview prediction grid test:

16 Interview Identities.
As each of the interview identities is the employers perception of the applicants ability to complete business-as-usual tasks, the generic opinion can easily change if the interviewee can improve either their perceived level of knowledge/experience or their level of confidence during the recruitment process.
By understanding the sixteen interview identities, job applicants can tweak how they confidently communicate their competencies to create one of the more positive identities’ that often results in job offers.
A detailed description of each interview identity can be found by taking the interview prediction grid test.

- Comes across as lacking the required skills and experiences for the role
- Has a low opinion on self
- Struggles to give detailed interview answers

- Struggles with challenging or technical interview questions
- Lacks industry related knowledge and experiences
- Gives short snappy answers

- May possess the required soft skills for the advertised role, but cant communicate any relevant experience in a way to gain a high-scoring answer
- Doesn’t always understand the meaning behind the interview question
- Gives answers that not relate to the job criteria

- Can be seen as suitable for low-skilled roles or for positions where the employer can support the employee, a level 2 apprenticeship as an example
- Answers are more detailed when talking about a personal experience, compared to answers for situational job interview questions
- Not as self-assured as some of the other interview identities

- A very confident communicator who will express themselves well, but who may hint to having skills and experiences that they don’t possess
- Struggles to answer technical interview questions due to a lack of industry experience/knowledge
- Doesn’t understand industry jargon and acronyms which can lead to answers that are irrelevant to the job interview question

- A highly confident interviewee who believes they are more suitable for the role than they actually are
- Skilled at self-promotion, but lacks the industry insights that is required to produce high-scoring interview answers
- Answers questions quickly, assertively and confidently, even when they don’t have the required criteria mention in the interview question

- Possesses enough sector-related experience to give detailed interview answers, but not enough prior experience for this to be consistent throughout the recruitment process
- Employers are often impressed with answers relating to personal skills and qualities, as the applicant is a self-promoter
- Struggles to recognise the job criteria for high-skilled roles

- A self-assured applicant who is consistent with their own self-promotion
- Lacks a deeper understanding of sector related models and theories that highlights, to the employer, their lack industry experience
- May argue a point with an employer, even when lacking industry knowhow

- Has a good level of industry knowledge, which is hidden away by their lack of ability to share their experiences
- Interview answers are often short and snappy, filled with filler words
- Employers initial opinions are negative due to the applicants lack of rapport
- The quality of interview answers is sporadic, with the applicant able to talk more in-depth about business-as-usual tasks, but struggles when the employer challenges them
- Some answers will promote a unique selling point, but others may self-disclose weaknesses
- Potentially, a highly-skilled worker, who may struggle from imposture syndrome

- A highly employable applicant, due to the a large amount of industry experience and academic qualifications, but struggles with their own self-esteem and confidence
- Interview answer’s are short , snappy and fast-paced in delivery with the applicant keen to get the interview over with
- Employers will recognize the wealth of industry expertise, but on the other the interviewer will be concerned about the candidates confidence levels and how that may effect the team once employed

- Answers are mixed, with some being technical and in-depth, while others lacking any real substance
- The candidate can come across as standoffish when the applicant doesn’t respond to follow up questions with a detailed reply. But can give enough evidence to show their range of job related skills
- A highly-skilled individual who will open up to a ‘warm’ interviewer, but can shut down when interviewed by a ‘cold’ employer

- Applicants are aware of their own abilities and expresses these well throughout the job interview
- Rapport is easy to build and employers often have an instant liking towards the self-assured interviewee
- Cam debate subjects, but cant persuade as well as some of the other high/high interview identities

- Able to communicate their competencies confidently throughout the recruitment process, with employers seeing potential from the interview start
- Can be argumentative when challenged on a particular subject or knowledge, which can be their undoing
- Has a strong presence, with the employer having a positive ‘gut’ feeling about the obviously highly-skilled applicant


- A high number of years in the industry and the easy to recognise specialist skills results in consistent job offers
- Consistently delivers strong interview answers with examples while stating industry models and sector processes
- A very confident applicant, but not being a the over top of the confident scale can, sometimes, effect the impact of their interview answers

- The highest level of knowledge/experience and highest level of confidence, out of all the 16 interview identities, does create regular job offers but not as consistently as the egocentric applicant would like
- A self-promote who can easily showcase their value while impressing the employer with their personality traits
- The self-absorbed characteristic and their inflated view of self can place seeds of doubt in the employer minds